|
|
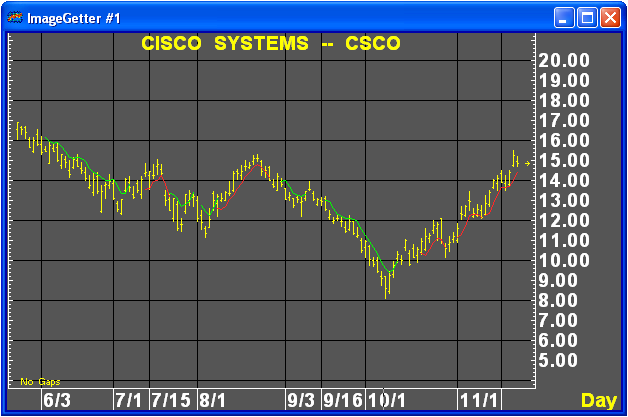
TD MA1 displays the moving average of highs and/or lows beginning with the current bar. The moving averages only appear once a new high bar or new low bar exceeds all highs/lows of a selected range of bars. TDMA I is helpful as an exit or as a stop loss indicator.
TD MA1 Parameters
This study draws interrupted moving average lines. Two moving averages are drawn, but only when particular conditions hold.
Moving average A is computed on the High prices (actually on any selectable price, but High would typically be used). Moving average B is computed on the Low prices (again selectable). Moving average type and length are selectable, but the same type and length parameters are used for both A and B.
The averages are computed continuously (this makes a difference for exponential averages, for example). But they are drawn only in intervals determined by the following conditions. A count parameter C and a length parameter L are used.
Line A begins to be drawn whenever the High price is strictly less than all C-1 preceding Highs. The line continues to be drawn while this condition remains true, and for L-1 additional bars when it ceases to be true. (No gap occurs if the condition becomes true again within L bars.)
Line B is drawn when the Low price is strictly greater than all C-1 preceding Lows. The line continues to be drawn while this condition remains true, and for L-1 additional bars when it ceases to be true.
Two scaling factors are provided, each of which scales the values of one line by an absolute multiple.
In addition, a "projection" (Proj.) factor is provided. This shifts the output to the right by X percent of the moving average length (rounded to the nearest integer number of bars). Both the MA computations and the determination of the drawing intervals are done in sync with the input data; the TD Price Projector simply delays the final output by some number of bars.
For further information on TDMA I, please refer to Thomas R. DeMark, The New Science of Technical Analysis, New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1994, Chapter 6, Moving Averages.